Applications of clinical High-b-values q-Space Diffusion-Weighted MRI (QSI) in White Matter Associated Disorders:
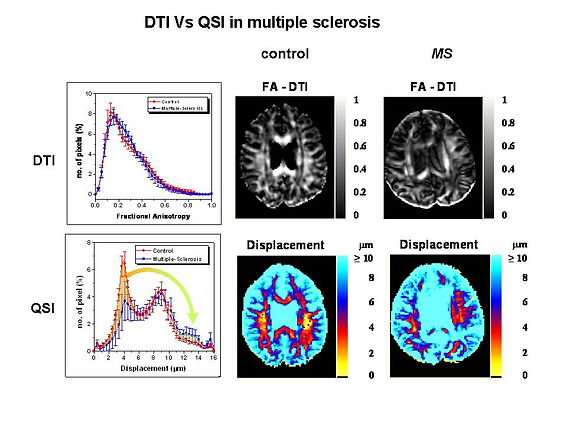
After demonstrating the high sensitivity of the high-b-values q-space diffusion MRI (QSI) to changes in axonal morphology, we anticipated that this approach will be useful for studying early white matter associated disorders also in human subjects. Indeed, this new imaging concept that was developed first in vitro, was carried out on human subjects using clinical scanners. Applications include neurodegenerative processes and white matter associated disorders such as multiple sclerosis (MS) and different types of dementias. Currently this technique seems to be superior to other MRI methods in use for evaluating the disease load in MS. QSI is also very efficient in determining whether normal appearing white matter (NAWM) is indeed normal.
Our preliminary results seem to suggest that this type of MR images has also the potential of differentiating between dementia of the Alzheimer type and vascular dementia (VaD). In this subject we intent to continue to expand the applications of this methodology to study brain maturation and other neurodegenerative disorders with the aim of increasing diagnosis specificity and in order to evaluate the efficacy of new drugs against these diseases.

